What Is Emergency Override — How It Works, Why It Matters, and When It Saves Lives is all about control, safety, and timing. In all automated worlds, systems will fail, but an emergency override allows humans to regain control.
If it is a pilot disengaging autopilot, a doctor engaging a manual override on life support, or a driver taking control of a self-driving car, this system saves lives. Seeing how emergency overrides function makes you realize how people and machines work together in the seconds that matter.
What Is an Emergency Override?

An emergency override is a system that lets a person bypass normal automated controls when something goes wrong. It acts as a backup that allows you to take charge when a machine or computer system stops responding or behaves unexpectedly.
These systems exist everywhere — in cars, airplanes, factories, hospitals, and even cybersecurity systems. When automation fails, an override restores human decision-making. Think of it as a safety net designed to protect people and property in emergencies.
How Does an Emergency Override Work?
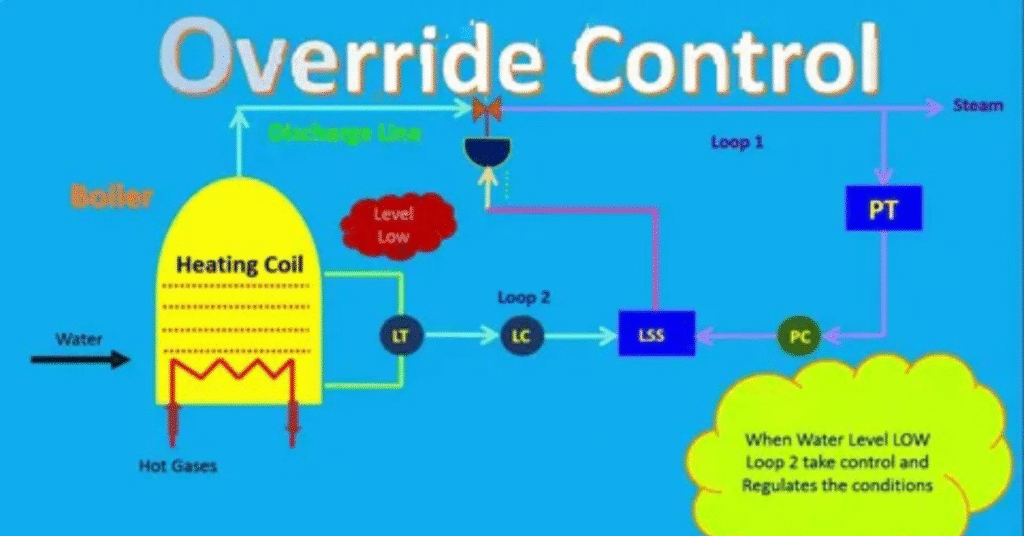
An emergency override system works by interrupting normal control processes. It either gives direct human control or activates a pre-set safety mode. The logic behind it depends on the type of system, but the goal is always to bypass automation safely.
For example, when an elevator stops due to a fault, an override key lets trained personnel open the door manually. In vehicles, pressing the brake overrides the cruise control instantly. In hospitals, backup generators start automatically when power fails — that’s also an override at work.
SEE MORE: https://doctorambulance.com/when-to-go-to-the-emergency-room/
| Type | Trigger Method | Example |
| Manual | Human-operated switch or key | Elevator door release |
| Automated | Software or sensor response | Power generator activation |
| Remote | Command from authorized personnel | Cybersecurity lockdown release |
Types of Emergency Override Systems

There are several types of emergency overrides depending on how and where they’re used. Mechanical overrides involve physical actions, like pulling a lever or turning a key. They’re often found in older systems or machinery that needs direct human intervention.
Electronic or software-based overrides use programmed commands or digital controls. These are found in modern industries — from driver assistance systems to industrial machines. Another kind is the automated safety override, which works without human input, like anti-lock braking systems or smart home fire safety triggers.
Importance of Emergency Override

The importance of an emergency override can’t be overstated. It ensures safety when automation fails or malfunctions. Machines are efficient but not perfect, and sometimes sensors misread data or systems crash. In such moments, an override prevents chaos.
It also maintains business continuity. In industries like aviation, healthcare, or manufacturing, downtime costs millions. Overrides allow quick recovery, protect human lives, and reduce property damage. In short, they’re the safety valves of modern automation.
Real-Life Examples of Emergency Overrides
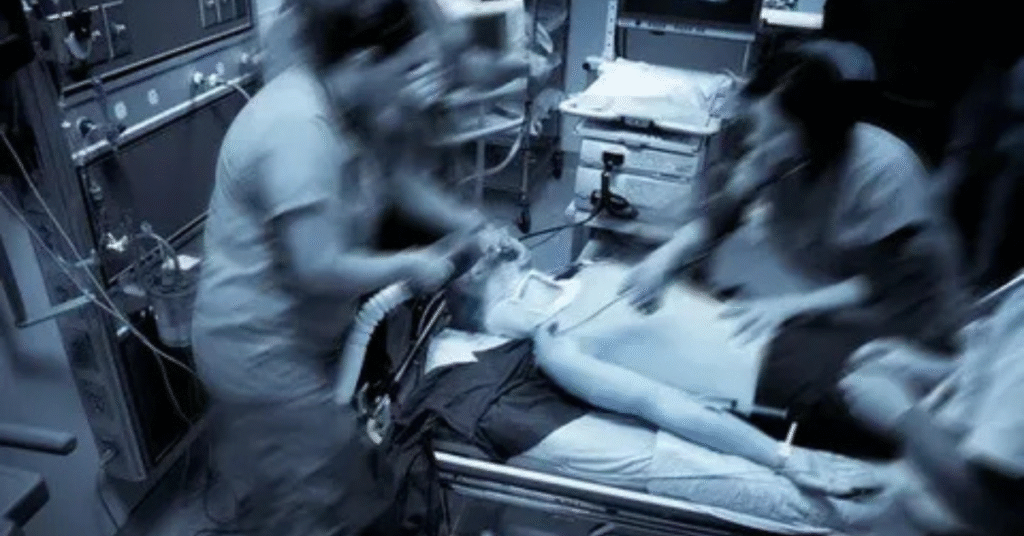
Real-world examples show how vital these systems are. In aviation, pilots often use manual overrides when autopilot fails or behaves unexpectedly. For instance, during turbulence, disengaging autopilot gives the pilot control to stabilize the plane.
In hospitals, life-support systems and ventilators have emergency overrides so doctors can switch to manual control during electrical faults. In vehicles like Tesla, the driver can override autopilot by steering or pressing the brake. These cases prove that overrides act as the final line of defense.
Risks and Safety Concerns

While emergency overrides are designed to save lives, they carry risks if misused or poorly designed. Human error is one major issue. A wrong decision made during panic can worsen a situation. Systems must therefore include clear labels, instructions, and training for staff.
Another growing risk is cybersecurity. Digital override systems connected to the internet can be hacked. An unauthorized override could disable safety systems or open secure access points. Proper encryption, restricted access, and regular system checks reduce such threats.
| Risk Type | Impact | Prevention |
| Human Error | Wrong activation or delay | Training and clear labeling |
| Technical Fault | Override failure | Regular maintenance |
| Cyberattack | Unauthorized control | Strong authentication |
Managing and Maintaining Override Systems

Proper management ensures reliability. Maintenance involves testing override switches, updating software, and replacing worn-out mechanical parts. Scheduled inspections are mandatory in industries like aviation and healthcare.
Staff training is equally critical. Operators must know when and how to activate the override without hesitation. Many organizations use simulation training to prepare staff for emergencies. This keeps systems efficient and reduces human-error risks during real incidents.
Legal and Ethical Considerations

The legal and ethical aspects of emergency overrides are gaining attention as automation grows. Regulations require overrides in all safety-critical systems. For instance, OSHA and ANSI set standards for industrial equipment, while the FAA mandates manual control options in aircraft.
Ethically, the debate focuses on who should control the final decision — human or machine. In AI-driven systems like self-driving cars, the question is: should the system act automatically or wait for human input? Balancing safety with accountability remains a challenge.
he Future of Emergency Override Technology

The future looks promising as technology evolves. Smart systems now use AI and IoT to predict failures before they happen. Predictive overrides can engage automatically, preventing accidents even before they start.
However, the core principle remains unchanged — keeping humans in control. Future systems will likely blend automation with human judgment, ensuring that even as machines get smarter, human intuition still holds the final say.
| Future Trend | Description |
| AI-Based Override | Predicts and prevents system failure |
| Cloud-Linked Safety Control | Allows remote manual overrides |
| Smart Training Systems | Uses VR to train operators for emergencies |
Case Studies of Emergency Override in Action

One famous case involves a Tesla Model S, where autopilot detected an obstacle late. The driver’s quick override by steering saved a collision. This highlighted why manual control must always remain available.
Another case occurred in a hospital during a city-wide blackout. Backup power failed to start automatically, but a manual generator overrides restored power to the ICU. These real stories show how emergency overrides save lives when systems fail unexpectedly.
Common Challenges in Emergency Override Systems

Even though emergency override systems are designed for safety, they come with several challenges. One major problem is balancing automation and manual control. Too much automation can reduce human alertness, while too little can slow response times in a crisis. Another issue is outdated equipment that may not respond quickly when an override is needed most.
Maintenance is also a big concern. Many organizations forget regular testing or skip software updates, which can lead to failure when an emergency happens. Without proper care, even the best-designed override can malfunction. The key is to combine smart technology with consistent training and regular inspection.
Training and Human Role in Overrides

The human role in an emergency override remains critical, no matter how advanced systems become. A well-trained operator can act faster and smarter than any automated system when seconds count. Training helps people understand not only when to activate an override but also how to handle the aftermath safely.
Many industries use simulations to prepare their teams for real-life situations. For example, pilots train in flight simulators to practice manual overrides during turbulence or system errors. The goal is to build confidence and ensure that when the unexpected happens, humans stay in control, not the machines.
CHEAK: https://doctorambulance.com/what-is-an-emergency-action-plan-a-complete-guide/
Emerging Technologies Improving Override Safety
New technologies are making emergency override systems more reliable and intelligent. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) can now detect early warning signs before a system breaks down. These smart overrides can predict potential risks and activate safety responses automatically.
For instance, modern vehicles use predictive systems that sense driver inattention and prepare the brakes in advance. In factories, smart sensors can trigger machine shutdowns before overheating occurs. The combination of data analytics and AI overrides a new layer of protection that was once impossible.
Balancing Automation and Human Control

Finding the right balance between automation and human control is the future of safety design. Automation increases efficiency, but it can never fully replace human judgment. A perfect system allows humans to override automation instantly when they sense danger or malfunction.
In critical environments like aviation or healthcare, this balance saves lives. Too much dependence on machines can cause slow reactions, while too little automation can overwhelm humans. The best emergency override systems blend both — using automation for speed and humans for wisdom.
FAQ”s
What is the purpose of an emergency override?
It allows humans to take control when automated systems malfunction or behave unpredictably.
Are emergency overrides manual or automatic?
They can be both. Manual overrides need human action, while automatic ones trigger based on sensors or system logic.
Where are emergency overrides used?
They’re used in vehicles, elevators, factories, hospitals, aircraft, and computer systems.
What are the main risks of using an override?
Risks include human error, unauthorized access, and mechanical failure if not maintained properly.
How often should override systems be tested?
Testing should happen regularly — at least once every six months — to ensure reliability and compliance with safety standards.
Conclusion
What Is Emergency Override — How It Works, Why It Matters, and When It Saves Lives highlights how human control protects life and property in emergencies. These systems act as silent guardians, waiting to restore order when automation breaks down. As technology advances, keeping a balance between human intelligence and machine precision will remain essential for safety, reliability, and trust.