What Is Emergency Heat is a thermostat setting that offers secondary Many homeowners wonder what really means and when to use it.” when your primary pump can’t operate correctly. It’s typically called on in cold weather or system malfunction. When the outside unit cannot transfer heat any longer,
the system defaults to an internal secondary source such as electric coils or a gas furnace. This gets your home heated, but it costs more. Knowing enables you to bypass peak bills and protect your system from extreme cold.
How Heat Pumps Normally Work
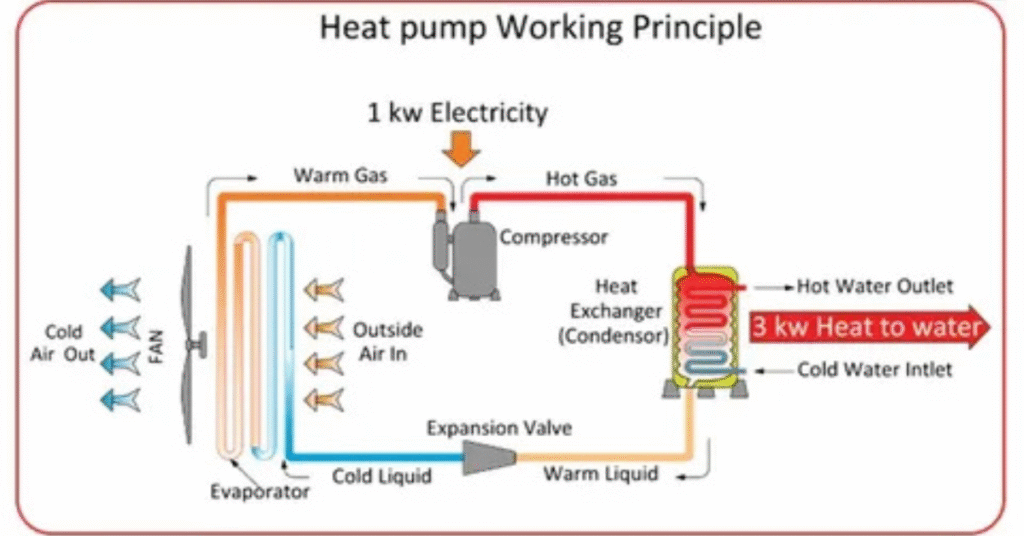
A heat pump doesn’t create heat—it transfers it. Even cold air outside contains heat energy. The pump extracts this warmth and moves it indoors. It uses a compressor, refrigerant, and coils to make this happen. However, when the outdoor temperature drops below freezing, the pump struggles to gather enough heat.
That’s when a backup source like extra heat mode mode comes in. It ensures you still get warmth when your main system can’t handle the load. But it’s not meant to run constantly, only when necessary.
Understanding Emergency Heat Mode

When you switch your thermostat to Many homeowners wonder what really means and when to use it.” Mode, the system bypasses the outdoor heat pump completely. Instead, it turns on an internal electric heater or furnace. This is called the secondary heat source. It provides heat instantly but consumes much more power.
extra heat mode is a manual setting. It’s not something your system turns on by itself. You use it when the outdoor unit freezes, breaks down, or can’t function due to extreme cold.
YOU WILL LIKE: https://doctorambulance.com/what-does-emergency-override-mean-understanding-its-importance-and-applications/
How Emergency Heat Works Step by Step
When you activate Many homeowners wonder what really means and when to use it.”, several things happen. First, your thermostat sends a signal to shut off the outdoor compressor. Then the indoor backup heater, either electric coils or a gas furnace, starts working. This backup heat doesn’t rely on outside air—it simply creates warmth directly.
This process is effective but costly. Because electric resistance heat uses more power, your electricity bill can rise quickly if you leave it on for days. secondary heatingshould only be used temporarily until your system is repaired or temperatures rise.
When to Use Emergency Heat

You should turn on only when the main heat pump stops working. If the outdoor unit freezes, gets damaged, or won’t start, it’s safe to switch to emergency mode. Another time to use it is when the outside temperature drops extremely low and the system can’t keep up with your thermostat setting.
Using this setting also prevents the compressor from overworking or getting damaged. But if you’re not sure what’s wrong, it’s better to call an HVAC technician for advice instead of leaving Many homeowners wonder what emergency heat really means and when to use it.”on for too long.
How to Turn On Emergency Heat Safely

To turn on locate the thermostat setting labeled “EMbackup heat ” Move the switch from ” to “EM Many homeowners wonder what backup really means and when to use it.”” You’ll notice the outdoor unit stops running while warm air starts coming from your vents.
Make sure to check for system warnings or fault codes before using it. If your backup pump frequently needs emergency mode, there might be an issue with the defrost system, refrigerant level, or thermostat sensor. In that case, it’s best to call a professional to inspect your unit.
Pros and Cons of Emergency Heat
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Keeps home warm when main unit fails | Uses a lot of electricity |
| Prevents system damage in freezing weather | Raises energy bills quickly |
| Works instantly as a backup heat source | Not meant for long-term use |
can be a lifesaver in a cold snap, but it’s not efficient. Regular maintenance helps reduce the need for emergency mode and saves you money over time.
Emergency Heat vs Auxiliary Heat

Many people confuse emergency heat with auxiliary heat, but they’re not the same. Auxiliary heat automatically kicks in when the outdoor temperature is too low for the heat pump to work efficiently. It supports the main unit but doesn’t turn it off.
Emergency heat, on the other hand, is manual. It completely shuts down the heat pump and relies only on the backup source. The table below shows the difference.
| Feature | Auxiliary Heat | Emergency Heat |
| Activation | Automatic | Manual |
| Outdoor Unit | Still runs | Shut off |
| Purpose | Support heat pump | Backup for failure |
| Efficiency | Moderate | Low |
Common Misconceptions About Emergency Heat

A big myth about emergency heat is that it makes your home warm faster. That’s false. It simply changes the source of heat, not the speed of heating. Another misconception is that it should be used whenever it’s cold outside. In reality, it’s meant only for emergencies or system breakdowns.
Some homeowners also think it’s the same as auxiliary heat, but as explained above, they work differently. Misusing secondary heating can lead to high energy bills and wear out your backup system faster.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips

Proper care keeps your emergency heating system reliable. Clean or replace air filters every 30 to 60 days to prevent airflow issues. Keep the outdoor unit free of snow, leaves, or debris. During winter, check the defrost cycle to ensure the unit isn’t freezing up.
Have a professional HVAC inspection at least once a year. Regular maintenance reduces breakdowns and helps your system run efficiently, so you won’t need emergency heat often.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Insights
Emergency heat costs far more to run than a standard heat pump. Electric resistance coils are only about 100% efficient, meaning every watt of electricity turns into one watt of heat. A heat pump, by comparison, can produce three watts of heat for every watt of electricity.
| System Type | Efficiency (COP) | Estimated Cost per Hour |
| Heat Pump | 3.0–4.0 | $0.30–$0.50 |
| Emergency Electric Heat | 1.0 | $1.00–$1.50 |
| Gas Furnace Backup | 0.9–0.95 | $0.70–$1.00 |
This shows why using emergency heat for long periods can dramatically raise your monthly bill.
When to Call a Professional

If your emergency heat keeps turning on automatically, it’s a sign of trouble. Frozen coils, low refrigerant, or damaged compressors may be to blame. Call an HVAC technician if you notice weak airflow, strange smells, or frequent system shutdowns.
An expert can test electrical connections, refrigerant levels, and thermostat settings. Regular inspections help you avoid costly damage and ensure your backup system works when you truly need it.
How Weather Affects Emergency Heat

Extreme weather plays a big role in how often you need emergency heat. When temperatures drop below freezing, your heat pump struggles to pull warmth from the outside air. As a result, your thermostat may signal the need for backup heating to keep your home comfortable. This often happens during cold snaps or snowstorms when the outdoor unit can’t perform efficiently.
Heavy ice, strong winds, or freezing rain can also damage the outdoor coils and fan motor. When that happens, switching to emergency heat mode protects your system from strain until repairs are made. It’s best to inspect your outdoor unit regularly during harsh winters to prevent long-term issues.
SEE MORE: https://doctorambulance.com/what-is-the-treatment-for-high-vitamin-b12/
Smart Thermostats and Emergency Heat Control

Smart thermostats can make managing emergency heat much easier. They can automatically detect when your heat pump is struggling and alert you before a failure occurs. Some models even send maintenance reminders or warnings if the system enters emergency mode too often.
With a smart thermostat, you can monitor energy use, switch modes remotely, and keep your heating system running efficiently. Using smart controls helps reduce energy waste and ensures emergency heat activates only when truly necessary.
Final Thoughts on What Is Emergency Heat

Knowing what emergency heat is helps you make smarter heating decisions in winter. It’s your system’s safety net, not a daily heating solution. Keep your equipment clean, test it before cold weather arrives,
and always call a professional when something feels off. Proper care ensures your emergency system works when you need it most and keeps your home safe, warm, and energy-efficient.
FAQ”s
What is emergency heat used for?
It’s a manual backup heating mode used when your heat pump fails or can’t keep up in freezing temperatures.
Is emergency heat the same as auxiliary heat?
No. Auxiliary heat turns on automatically, while emergency heat is manually activated when the outdoor unit isn’t working.
Can I leave the emergency heat on all night?
Yes, but only if necessary. Leaving it on for long periods increases your electricity costs.
Why is emergency heat so expensive?
Because it relies on electric resistance heating, which consumes a lot more power than a heat pump.
How do I know if my system is in emergency mode?
Your thermostat will display “EM HEAT,” and the outdoor unit will stop running while warm air continues inside.
Conclusion
What Is Emergency Heat is a vital backup system that keeps you safe and warm when your main heat pump fails. However, it’s not meant for long-term use because it consumes more energy and increases your bills.
Use it only in emergencies, maintain your system regularly, and schedule professional checkups before winter. Understanding how secondary heating works saves money and ensures comfort when the temperature drops.