What is an Emergency Action Plan? Knowing this is essential for any business and workplace. An General explanation part is a written document that details how employees and employers must act during emergencies. It provides safety, reduces risk, and assists companies to recover faster.
An awareness of the steps, elements, and advantages of an General explanation part could save lives and safeguard property. In this guide, you shall discover how to create, execute, and update a successfulWhen talking about offices or job sitesthat meets safety regulations and equips your team for anyWhen talking about offices or job sites.
Definition of an Emergency Action Plan

An Emergency Action Plan is a structured plan designed to guide organizations during emergencies. It provides clear instructions for employees on what to do in case of a fire, natural disaster, chemical spill, or medical emergency. Unlike general safety rules, an emergency action plan is proactive, detailed, and specific to the workplace. It identifies hazards, assigns responsibilities, and outlines procedures to prevent chaos during an incident.
Understanding the definition of an emergency action plan is crucial because it sets the foundation for workplace safety. Without a well-drafted plan, employees may panic, evacuation routes may be unclear, and critical resources may be mismanaged. In short, an emergency action plan is the backbone of a safe and prepared workplace.
Key Components of an Emergency Action Plan
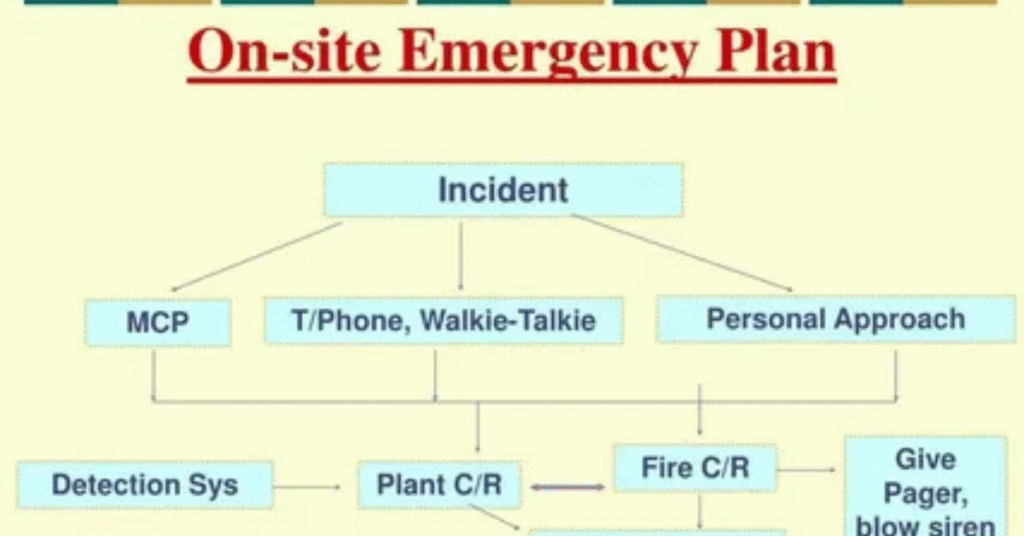
An effective Emergency Action Plan contains several key components. It includes emergency contacts, a chain of command, and clear roles for every employee. The plan must detail evacuation routes, emergency exits, and safe shelter areas. It should also cover communication protocols, emergency supplies, and procedures for different scenarios.
For example, during a fire, employees need to know who to report to, which exits to use, and how to assist visitors. During a chemical spill, trained personnel must know how to contain the hazard and whom to notify. Table 1 below shows a simple structure for an emergency action plan.
YOU WILL LIKE: https://doctorambulance.com/what-is-emergency-heat-a-complete-homeowners-guide/
| Component | Purpose | Example |
| Emergency Contacts | Immediate communication during crisis | Fire department, HR, Manager |
| Evacuation Routes | Safe and quick exit from the building | Marked staircases, exits |
| Roles & Responsibilities | Defines tasks for employees during emergencies | Fire wardens, first aiders |
| Communication Plan | Internal and external notifications | Text alerts, loudspeakers |
| Emergency Supplies | Necessary tools and equipment | Fire extinguishers, first aid kits |
Types of Emergencies Covered

An Emergency Action Plan must cover multiple types of emergencies. These include fires, medical emergencies, chemical spills, natural disasters, and workplace violence. Each type has unique risks and requires specific responses. Fires demand immediate evacuation and alarm activation. Chemical spills may require containment and protective gear.
Real-world examples highlight the importance of covering all types. In 2019, a factory fire in Texas forced employees to evacuate safely because their emergency action plan was well-designed. In contrast, a warehouse without a proper plan suffered property damage and injuries during a similar incident. Including multiple emergency types ensures readiness for any situation.
Steps to Develop an Emergency Action Plan

Developing an Emergency Action Plan starts with a thorough risk assessment. Identify potential hazards and the likelihood of each scenario. Next, draft procedures for each emergency, including evacuation, communication, and employee roles. Assign responsibilities clearly and ensure everyone understands their tasks.
Regularly reviewing and updating the plan is vital. Emergencies evolve, buildings change, and staff turnover occurs. A strong plan also includes feedback from drills and past incidents. Table 2 below shows a checklist to develop an emergency action plan.
| Step | Action |
| 1 | Conduct workplace risk assessment |
| 2 | Identify potential emergencies |
| 3 | Create detailed evacuation and response procedures |
| 4 | Assign roles and responsibilities |
| 5 | Establish communication plan |
| 6 | Conduct training and regular drills |
| 7 | Review, update, and improve the plan periodically |
Training and Communication

Training is a key part of any Emergency Action Plan. Employees must understand what to do during a crisis. Conducting regular drills ensures everyone knows their role. Communication should be clear, concise, and accessible. Use multiple channels like email, posters, text alerts, and loudspeakers to reach all employees.
Training should include new hires and refresher sessions for existing staff. Drills allow employees to practice evacuations and safety procedures without panic. Clear communication ensures that everyone, from management to staff, responds quickly and correctly, reducing injuries and chaos.
Legal Requirements and OSHA Standards

OSHA requires businesses to maintain an Emergency Action Plan. Regulations vary depending on industry, but all plans must ensure worker safety and compliance. Companies must document procedures, train employees, and review the plan regularly. Non-compliance can result in fines, penalties, or legal liability.
Industry-specific standards also apply. Chemical plants, hospitals, and schools may face stricter requirements than office buildings. Following OSHA and local regulations ensures legal protection and builds employee confidence. It also demonstrates a company’s commitment to safety and risk management.
Benefits of an Effective Emergency Action Plan
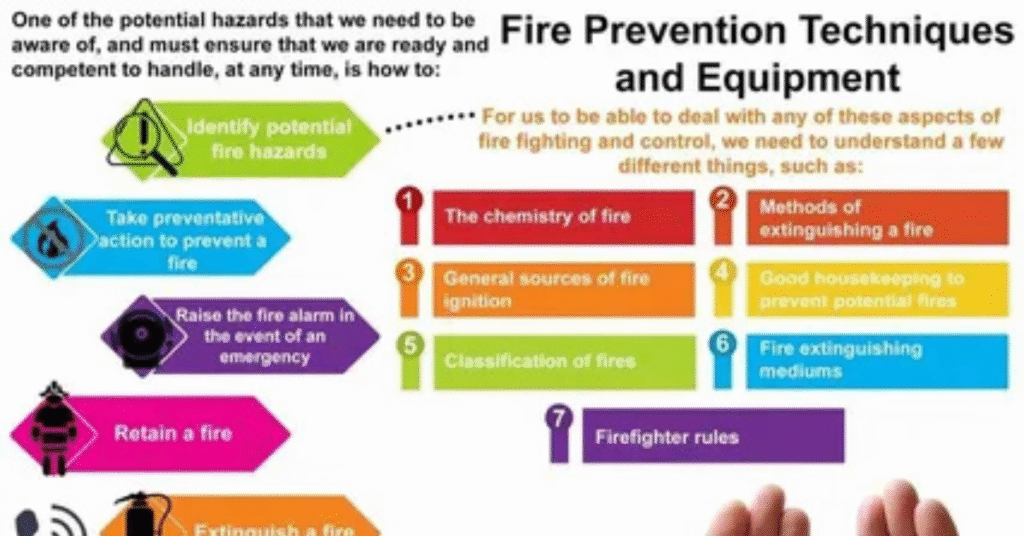
A well-crafted Emergency Action Plan saves lives, reduces injuries, and protects property. It ensures business continuity and minimizes downtime after an incident. Employees feel safer, which improves morale and productivity.
Case studies show the value of a good plan. In 2021, a manufacturing plant avoided major injuries because employees followed a detailed emergency action plan during a gas leak. In contrast, workplaces without plans experience confusion, higher injury rates, and financial loss.
Common Mistakes to Avoid

Many organizations fail to maintain an effective Emergency Action Plan due to avoidable mistakes. These include not updating the plan regularly, poor communication, ignoring training, and assigning unclear roles. Overcomplicating procedures can also create confusion during an emergency.
Simplifying processes, keeping the plan updated, and conducting regular drills prevents these mistakes. A practical, easy-to-follow emergency action plan ensures everyone knows exactly what to do when seconds matter.
Monitoring, Reviewing, and Improving the Plan

An Emergency Action Plan is not static. Businesses must monitor drills, review incidents, and incorporate lessons learned. Feedback from employees highlights weaknesses in procedures. Regular audits and evaluations help improve evacuation routes, communication, and response times.
Continuous improvement ensures the plan adapts to new hazards, changes in personnel, and technological advancements. A plan that evolves with the workplace remains effective and reliable in protecting lives and assets.
Tools and Resources for Creating an Emergency Action Plan
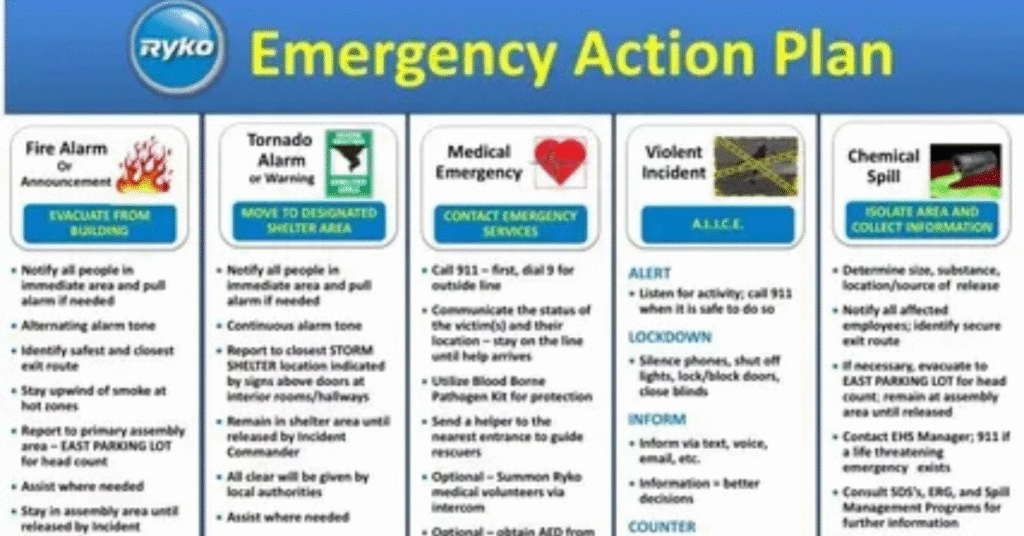
Creating an Emergency Action Plan is easier with the right tools. Software, templates, and mobile apps help streamline planning, documentation, and communication. Government resources, OSHA guidelines, and professional consultants provide expert advice.
For example, OSHA offers sample plans and checklists for small businesses. Some companies use digital tools to track drills, update procedures, and notify employees instantly. Using these resources ensures a practical, compliant, and efficient emergency action plan.
Emergency Action Plan Checklist
| Task | Status | Notes |
| Risk assessment completed | Yes/No | Include all potential hazards |
| Roles assigned | Yes/No | Define responsibilities clearly |
| Evacuation routes posted | Yes/No | Include maps and accessible exits |
| Employee training conducted | Yes/No | Include new hires and refresher sessions |
| Communication plan tested | Yes/No | Use multiple channels |
| Plan reviewed and updated | Yes/No | Annually or after incidents |
Real-Life Case Studies

A chemical plant in Ohio prevented major injuries during a leak because the employees followed a detailed emergency action plan. Their plan included evacuation procedures, communication, and protective gear.
Another example is a school in California that avoided chaos during a fire by conducting monthly drills, which ensured students and staff evacuated safely. These cases show that planning and practice save lives.
Final Tips for a Strong Emergency Action Plan
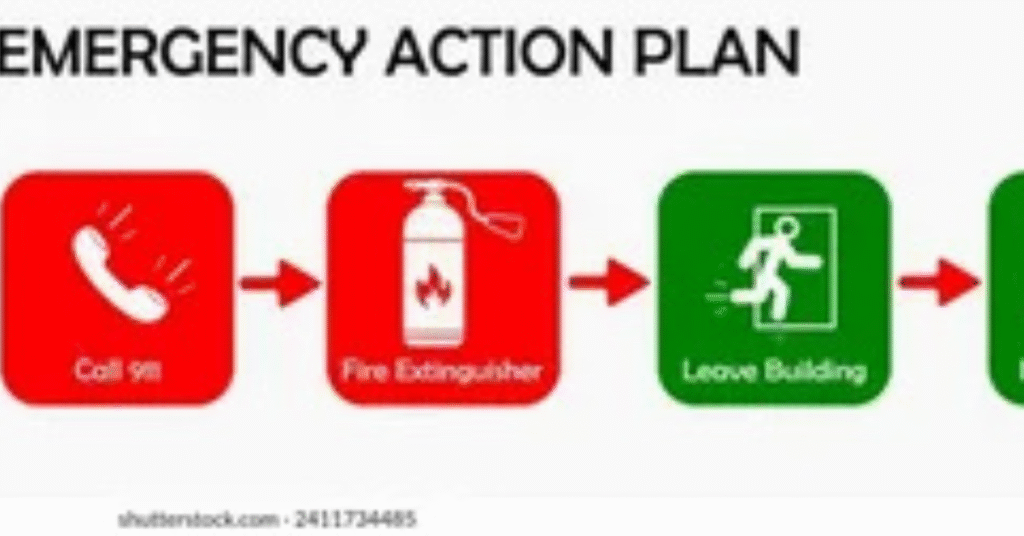
Keep the plan simple, clear, and updated. Train employees regularly and practice emergency drills often. Use technology and resources to streamline communication.
Make safety a priority, not an afterthought. Remember, seconds matter during emergencies, and a well-prepared team can make all the difference.
FAQ”s
What is an Emergency Action Plan?
It is a written plan that guides workplace safety and emergency response.
Who needs an Emergency Action Plan?
All businesses, regardless of size, should have one to protect employees and property.
How often should the plan be updated?
Review and update at least once a year or after major changes in the workplace.
Are drills required?
Yes, OSHA recommends regular drills to ensure all employees understand procedures.
What types of emergencies should the plan cover?
Fires, medical emergencies, chemical spills, natural disasters, and workplace violence.
Conclusion
What is an Emergency Action Plan? It is a vital roadmap for workplace safety. An effective plan saves lives, reduces injuries, and protects property. It ensures business continuity and builds confidence among employees.
Regular updates, training, and monitoring are crucial. By following a clear, well-structured emergency action plan, businesses can face crises with confidence and minimize risks effectively.